A Rare Opportunity
Rare earth elements are used in many high-tech applications in small volumes but are critical to performance. Demand is growing rapidly with the transition to renewable power generation.
What are Rare Earth Elements?
- Rare earth elements comprise 15 lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium
- Used in many high-tech applications in small volumes but are critical to performance
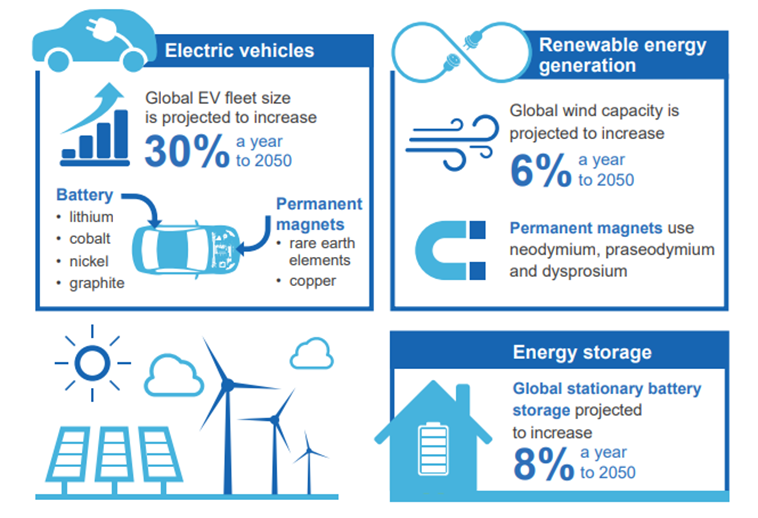
- Demand for Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) permanent magnets used in electric vehicles and wind turbines, will support prices for Neodymium (Nd), Praseodymium (Pr), Dysprosium (Dy) and Terbium (Tb)
TRANSITION TO RENEWABLE POWER GENERATION 200kg NdPr Oxide per 1MW of wind generation capacity
- Each direct drive wind turbine uses a permanent magnet motor that generates between 2-6MW of performance
- Each megawatt requires approx. 200kg pure NdPr Oxide
- Wind turbines anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 17% through to 2025
MASS PRODUCTION OF EVS HAS COMMENCED
Behind every battery is an electric Motor
- Over 90% of all EVs will be equipped with an NdFeB permanent magnet
- Each EV consumes an incremental ~1kg of NdPr Oxide
- EVs anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 29% over the next five years
- Hydrogen vehicles also reliant on permanent magnet motor technology
- Hydrogen vehicles also anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 11%through to 2025
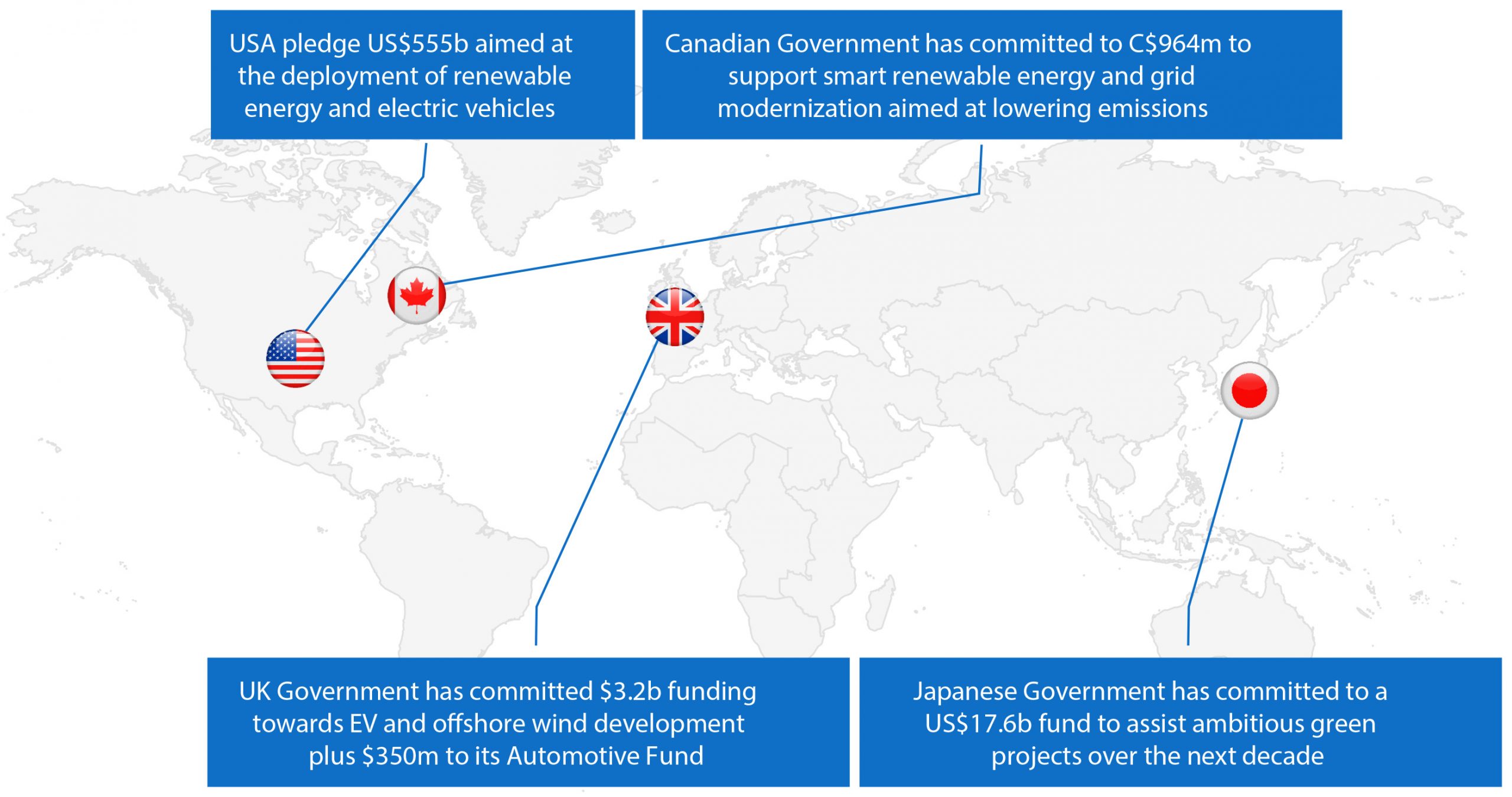
Global Decarbonisation and Electrification builds momentum
100+ countries have pledged to reduce methane emissions by 30% by 2030
- 190 countries and organisations have committed to phase out coal generated power
- 20 countries have committed to cease funding oil, coal and gas projects by the end of 2022
- 5 large public banks, including the European Investment Bank have committed to cease funding oil, coal and gas projects by the end of 2022
- 30+ countries and dozens of states and cities have committed to the phase-out of the sale of new internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles by 2035
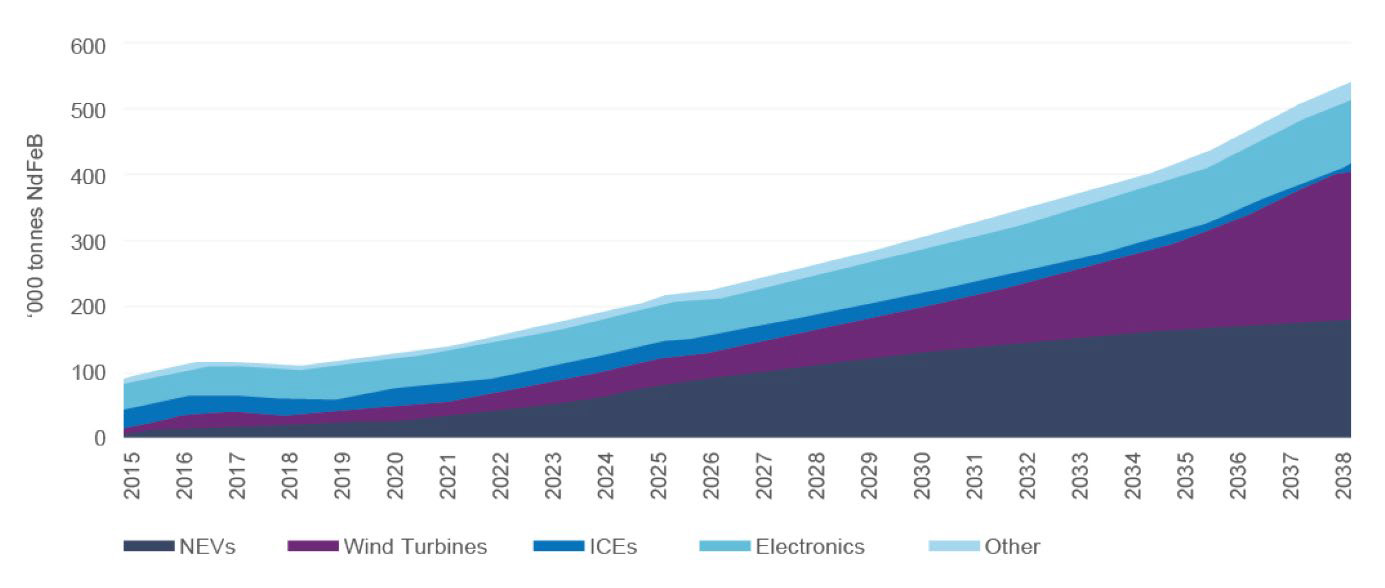
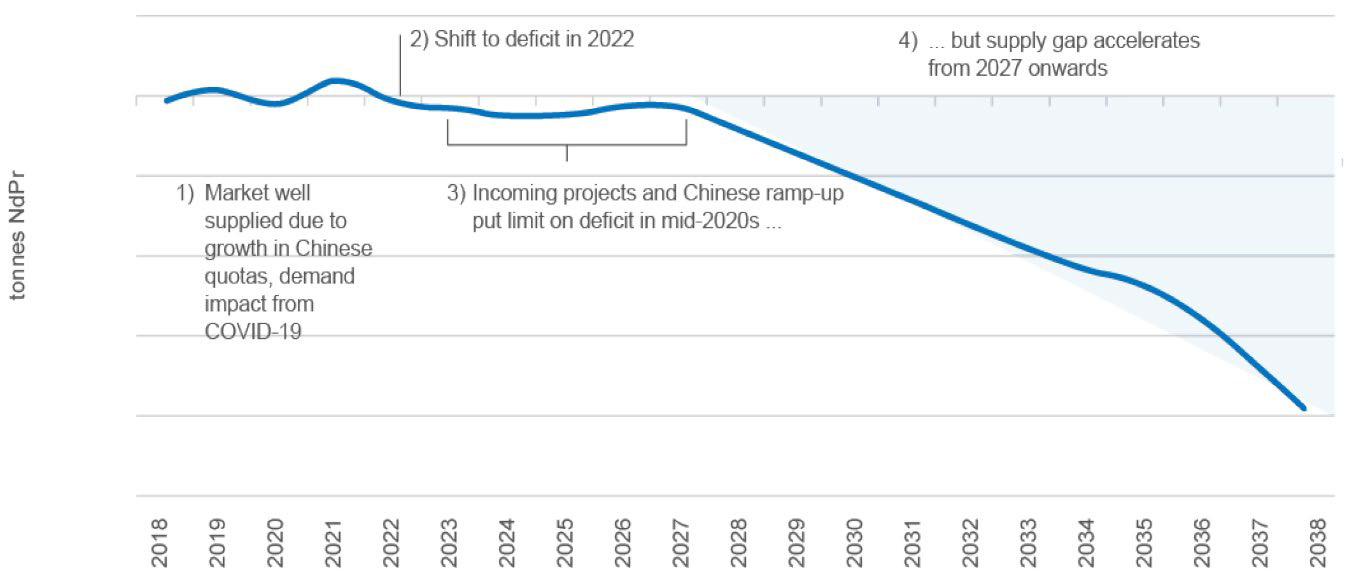
Strong Demand for both Neodymium and Praseodymium will result in a supply deficit over coming decade
Securing Supply Chain Reliability
Critical minerals are metals and non-metals that have important economic functions, cannot be easily substituted and face some degree of supply risk. Supply risks can stem from geological scarcity, geopolitical issues, trade policy or other factors, resulting in critical mineral lists differing by jurisdiction.
Critical minerals typically have an important role in industrial applications, but it is their vital, and rapidly growing, role in new technologies that is sparking interest and expectations of faster demand growth.
Economic security and supply-chain reliability is also driving attention in critical minerals, as some governments look to avoid the negative impacts of trade dependence and related market shocks.
Increasing awareness of mineral sourcing ethics, including environmental and social impacts, is driving further interest in mineral supply chains (e.g. EU battery regulations and industry led cobalt traceability measures).
Permanent rare earth magnets are used extensively in low-emissions technologies like wind turbines and electric vehicles, and the forecast demand is expected to grow.
The average annual growth for the price of magnet metals over the next 10 years to 2030 (in real terms) is projected to be 8-9% (Figure 4). The global rare earths market was valued at around US$2 billion in 2020, and is forecast to grow to around US$12billion by 2030, up an average 16% a year.